
How to Choose the Right Keywords for SEO

Mike Stuzzi
August 25, 2023
Want to know how to choose the right SEO keywords? This keyword selection guide covers it all
 Now more than ever, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a pivotal force that can make or break a website's online success. At the heart of SEO lies the strategic use of keywords – those powerful words and phrases that unlock the doors to higher rankings on searches and more organic traffic.
Now more than ever, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a pivotal force that can make or break a website's online success. At the heart of SEO lies the strategic use of keywords – those powerful words and phrases that unlock the doors to higher rankings on searches and more organic traffic.Imagine you have a treasure map with each keyword representing a shining gem that leads your target audience directly to your virtual doorstep. Understanding the art of choosing the right keywords is quite like possessing such a map. It guides you through the complexity of search engine algorithms and helps you reach the top rankings for your chosen keywords.
This guide aims to demystify keyword research and provide information on selecting the most effective keywords in your SEO endeavors. It doesn’t matter whether you’re an aspiring blogger, a seasoned marketer, or a business owner seeking to boost your online presence. Mastering keyword selection will be the key to unlocking your website’s full potential.
Tips for Selecting the Right SEO Keywords
Below, you’ll find information on proper keyword selection without spending much time, effort, or money.
1. Consider Your Target Audience
When it comes to finding the right keywords for SEO, considering your audience is an essential and often overlooked aspect of the process. Keywords act as the bridge that connects your content to the users actively searching for information, products, or services online. If you understand your audience, you can easily select keywords that align with their preferences, needs, and search behavior.
There are several ways to understand your desired audience's needs and choose relevant keywords to reach them. They include the following:
- Competitor analysis: This is a widely used method for many website niches that involves analyzing your competitors' marketing efforts and the audience they’re targeting. You may identify gaps in their strategies and opportunities to differentiate yourself by catering to underserved segments.
- Buyer personas: If you’re selling a product or service, this is where you create detailed buyer personas representing your ideal customers. These fictional characters embody specific traits, goals, and challenges of different audience segments, making it easier to tailor your content and SEO efforts.
- Market research: Here, you conduct comprehensive market research to identify the demographics, behaviors, and preferences of your potential customers. Use surveys, focus groups, and interviews to gather data about their interests, challenges, and purchasing habits.
- Website analytics: If you already have some traffic, it’s wise to analyze your website's traffic data using tools like Google Analytics. This data can reveal valuable information about your audience, such as their geographical location, browsing behavior, and device use.
2. Look at the Search Intent
Even after an in-depth understanding of your audience and their needs, you’ll need to use specific keywords for each piece of content you publish. Search intent refers to the underlying motivation behind a user's search query – what they are trying to achieve or find when typing a specific set of words into a search engine. Paying attention to user intent will help your content get in front of the right eye and boost your conversions.
Below are the different types of search intent:
- Informational intent: Users with informational intent seek answers, explanations, or information about a particular topic. They may use keywords like "how to," "what is," "tips for," etc. Understanding informational intent helps you create comprehensive guides, tutorials, and blog posts to address users' questions.
- Navigational intent: In this case, users seek a specific website or brand. They directly enter the name of the website or brand into the search bar. While navigational keywords like “[company name] email address” may not be relevant for SEO purposes, they’re vital for brand recognition and monitoring your online presence.
- Commercial intent: Commercial intent is whereby users are interested in purchasing a product or service but may still be in the research phase. Keywords like "best," "reviews," "compare," and "deals" indicate commercial intent. Optimizing for commercial intent helps attract potential customers early in the buying process.
- Transactional intent: Users with transactional intent are ready to make a purchase. They use keywords like "buy," "discount," "order," or "coupon" to find a specific product or service. Targeting transactional keywords helps capture users who are close to completing a purchase.
Useful Tip on Finding the Search Intent
If you aren’t sure about the intent of a specified keyword, look at the search results for your target keywords to understand the content that ranks well. If the top results are mainly blog posts or guides, it indicates informational intent. In case the results show product listings and e-commerce sites, it suggests commercial and transactional intent. Understanding SERPs helps you tailor your content to match user expectations.
Check the example below involving a search about “video editing apps.”
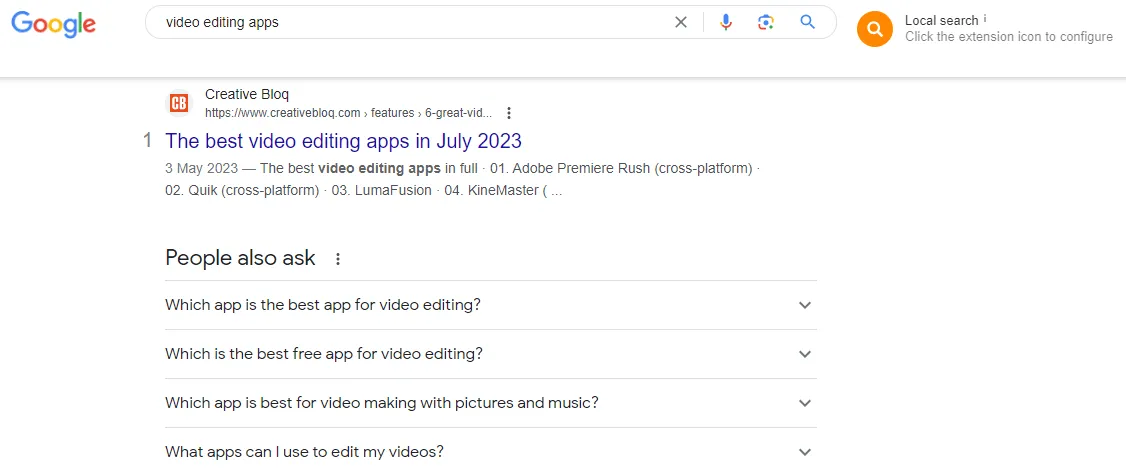
Initially, you may think the searcher wants to know what video editing apps are. But in the actual case, they’re looking for video editing app options. You can see that the People Also Ask section has some FAQs with terms like “best,” meaning that the intent is commercial.
Having identified the search intent behind your target keywords, you need to create content that satisfies those intentions. For informational intent, focus on in-depth guides and valuable information. For commercial intent, include product reviews and comparisons. For transactional intent, provide clear calls-to-action and easy paths to purchase.
3. Check the Traffic for Each Keyword
Keyword traffic refers to the search volume or frequency with which a particular keyword is searched on search engines over a specific period. Analyzing keyword traffic helps you identify the popularity and potential of keywords to drive organic traffic to your website.
For instance, if you’re a new blogger, you may be tempted to go with a keyword people aren’t searching for because it’s easier for you to rank. If people aren’t searching for the terms you’ve included in your post, be sure that it will get little traffic, if any.
According to Semrush, a good keyword should receive 100 searches a month at minimum. You could go for a keyword with traffic ranging from 100 to around 3,000 searches as a new site and get good traffic. In fact, targeting several of these small but high-potential keywords can help grow your overall site traffic with time.
4. Prioritize Long-Tail over Short-Tail Keywords
Prioritizing long-tail keywords over short-tail keywords is a strategic approach that offers several advantages for your SEO efforts. Long-tail keywords are more specific, usually consisting of three or more words, whereas short-tail keywords are shorter and more generic phrases.
The thing about long-tail keywords is that they provide a clearer indication of what users are looking for. As they are more specific, they align better with user intent.
When users find content that precisely matches their search query, they are more likely to engage with it. This leads to lower bounce rates and higher user satisfaction.
What’s more, short-tail keywords often have higher competition due to their broad nature. As a result, it can be challenging to rank well for them, especially for new or smaller websites.
Long-tail keywords, on the other hand, have less competition due to their lengthiness. You get a better opportunity to secure higher rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs).
How to Find Long-Tail Keywords
True to say, short-tail keywords are random and could be almost any word or phrase you can think of, such as “WordPress,” “zodiac signs,” or “men's fashion.” Long-tail keywords combine short-tail keywords with more words. They’re thus harder to find.
You can find long-tail keywords for free using Google’s autocomplete feature. When you type in something like “gaming console,” you can see more ideas of longer keywords people search for.

You can also find long-tail keywords from the People Also Ask and Related Searches sections of any Google search result page.
Another way to find long-tail keywords is to use a keyword research tool that provides a variety of metrics for keywords. A good example is Semrush, which has a free version and a trial period for new users. With its Keyword Overview tool, you can find longer keywords from any seed keyword you search for.
Below is an example with “AI software” as the seed keyword:
You see that it provides you with comprehensive keyword data along with more keyword ideas and questions with smaller difficulty scores.
5. Know Your Competition
As much as some keyword research tools show you how likely you are to rank for a specified keyword, it isn’t a guarantee. Knowing the competing pieces of content on the top results and using them as a reference for choosing keywords helps a lot.
If you didn’t already know, website authority influences the chances of one site ranking over another. The most established sites can usually appear on searches for millions of keywords.
If your site is new, the domain authority (DA) will likely be anywhere from 0 to 10. Sites that have been around for a while have a DA of about 30 to 40. Anything over 50 is well-established or has been actively building its backlink profile.
A tip here is that you can search your preferred keyword and then look at the competing sites. If your DA is less than 20, you could make sure that you at least see sites of similar DA or a bit higher. This means that you could also easily rank if you write content around the selected primary keyword.
6. Don’t Forget about the Profit
While writing as many informational posts as possible is a good SEO practice, you also need monetizable keywords. These keywords are the ones that will drive potential buyers or action-takers to your site.
If you only target informational keywords, you’ll get good traffic, which is hard to monetize. Most users will be searching for tips, advice, or entertainment and not necessarily looking to buy or sign up for anything.
That’s why you’ll also need to write content with transactional keywords. When doing keyword research, pay attention to keyword metrics like cost per click (CPC). Higher CPC means that advertisers are willing to pay more, and it’s thus a sought-after keyword.
You can monetize transactional-based content through selling your products and services or affiliate marketing. These two website monetization methods are highly lucrative and can generate significant revenue.
Conclusion
When trying to rank for specific search terms, selecting appropriate keywords is crucial. Unless you don’t need the traffic to convert, avoid going with keywords that are too broad and non-specific.
Long-tail keywords are the best choice since fewer people create content around them. Be sure to analyze the competition to know what they’re doing right and even spot gaps you can exploit with better content.
Once you’ve found your keywords and started to rank, feel free to use AccuRanker as your rank-tracking tool. It provides you with deep insights into SERPs and gives you ideas on how to improve your rankings for more traffic and conversions.
Related blog posts

5 LLM Visibility Metrics You Should Track in 2026
SEO is now both about ranking in search engines and being visible in LLMs. We give you five visibility metrics every SEO should track in 2026.
3 December 2025Is LLM Tracking Relevant for You?
LLM tracking is not just for SEOs. It is also relevant for content teams, agencies, marketing leadership, and communication teams. Learn why here.
26 November 2025
How to Find the Best Prompts to Track for AI Visibility
Do you want to start tracking prompts to optimize your AI visibility? We give you seven practical ways to identify relevant prompts to track in LLMs.
9 November 2025
